Science 6.9
Force, motion, and energy. The student knows that the Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it just changes form. The student is expected to:
(A) investigate methods of thermal energy transfer, including conduction, convection, and radiation;
(B) verify through investigations that thermal energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer to cooler until all the substances attain the same temperature such as an ice cube melting; and
(C) demonstrate energy transformations such as energy in a flashlight battery changes from chemical energy to electrical energy to light energy.
- Plus Plan

Thermal Energy Transfer: Solar Oven - STEM Project
A STEM project to use when learning about thermal energy transfer.
- Plus Plan
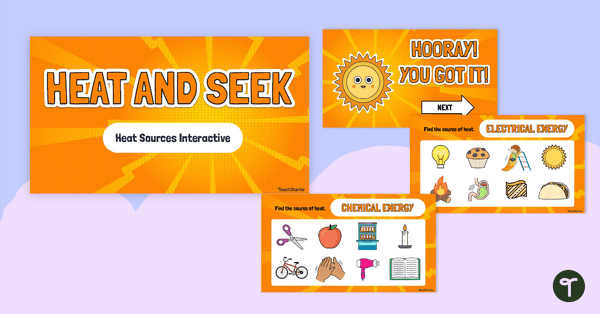
Heat Energy Sources Interactive Activity
Help students identify different sources of heat energy with this engaging, interactive activity.
- Free Plan
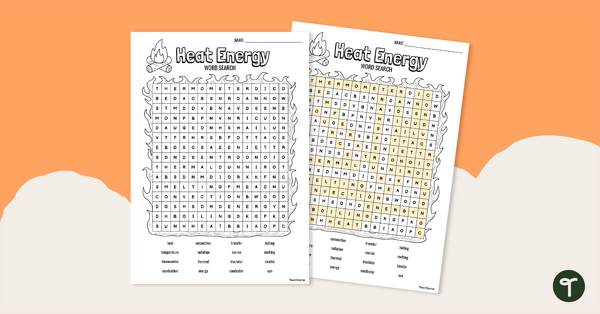
Thermal Energy Word Search
Help students remember heat energy vocabulary with this word search.
- Plus Plan
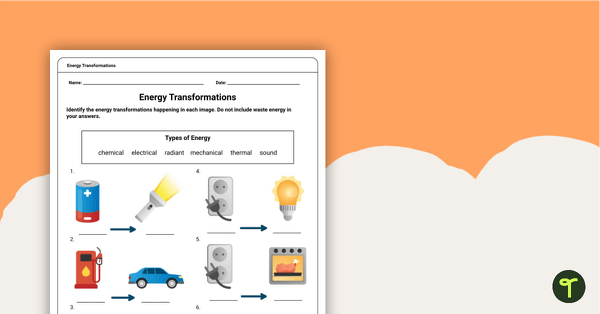
Energy Transformations Worksheet
A worksheet to practice identifying energy transformations.
- Plus Plan

Wheel of Heat Transfer Project
Explore the process of heat transfer with this engaging wheel of heat project.
- Plus Plan
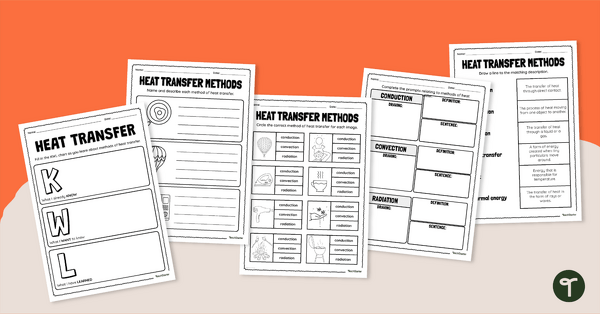
Heat Transfer Methods Worksheet Pack
Learn about the different ways heat can be transferred using this guided set of heat transfer worksheets.
- Plus Plan
Heat Transfer Posters
Display these posters to check understanding or reinforce the teaching and learning of how heat energy transfers.
- Plus Plan
What is Heat? Poster
Explore the concept of heat energy with this classroom poster.
- Plus Plan

Thermal Energy Movement Teaching Slides
Explore thermal energy, the movement of particles, and the effect on the state of matter with your students using these teaching slides and guided notes.
- Plus Plan

Heat Transfer Worksheet
A worksheet to practice identifying the methods of heat transfer.
- Plus Plan

Thermal Energy Transfer Sorting Activity
Learn about conduction, convection, and radiation with this set of 24 sorting cards.
- Plus Plan

All About Heat Transfer
Challenge your students to show what they know about conduction, convection, and radiation by identifying examples of each.
- Plus Plan
Thermal Energy Transfer Foldable
A foldable to use when learning about the three types of thermal energy transfer.
- Plus Plan

Observing Conduction Science Experiment
Teach students to make predictions about and observe thermal energy transfer through this conduction experiment.
- Plus Plan

Radiation Sorting Activity
A set of 20 cards to sort according to the type of electromagnetic wave.
- Plus Plan

Heat Transfer: Radiation Guided Notes
A set of guided notes to use when teaching about radiation.
- Plus Plan
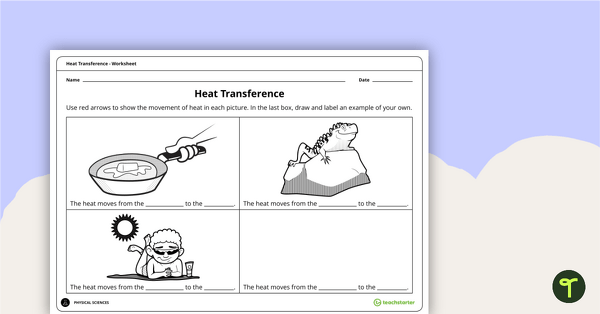
Heat Transference Worksheet
A worksheet to help students identify examples of heat transference.
- Plus Plan
The Heat is On Unit Plan
This science unit addresses the concept of heat energy, including heat sources, heat transfer, thermal conductors, and thermal insulators.