A poster explaining how to activate prior knowledge before reading.
Display this teaching resource in your classroom to remind students how to activate their prior knowledge before reading.

A poster explaining how to activate prior knowledge before reading.
Display this teaching resource in your classroom to remind students how to activate their prior knowledge before reading.

We create premium quality, downloadable teaching resources for primary/elementary school teachers that make classrooms buzz!
Would you like something changed or customised on this resource? While our team makes every effort to complete change suggestions, we can't guarantee that every change will be completed.
Did you spot an error on this resource? Please let us know and we will fix it shortly.
Are you having trouble downloading or viewing this resource? Please try the following steps:
If you are still having difficulty, please visit the Teach Starter Help Desk or contact us .

A fun game for students to play in small groups to consolidate their understanding of adjectives.
A fun game for students to play in small groups to consolidate their understanding of adverbs.
A set of 12 Queensland Cursive entry and exit shuttles to join together to make a handwriting spaceship.
44 Bloom's Taxonomy fast finisher activity cards.

A fun game for students to play in small groups to consolidate their understanding of verbs.
A set of 12 Queensland Cursive entry and exit shuttles to join together to make a handwriting spaceship.
A set of 12 Queensland Cursive entry and exit shuttles to join together to make a handwriting spaceship.

Amazing Man helps students to learn what both direct and indirect speech entails as well as providing examples on how they can use it themselves.
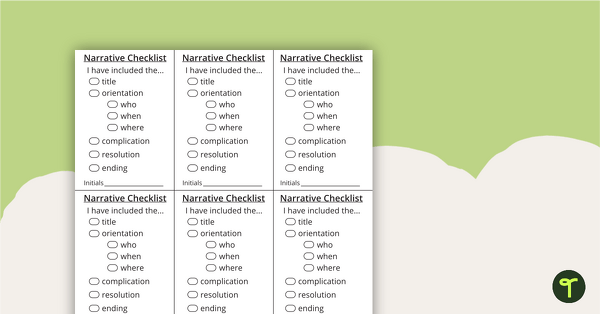
Use these Writing Checklists to ensure that your students have everything they need in their pieces of writing.

Lower Grade Desk Plates with the alphabet, number line and student's name on them.
0 Comments
Write a review to help other teachers and parents like yourself. If you'd like to request a change to this resource, or report an error, select the corresponding tab above.