A set of five literacy rotation task cards to be used in conjunction with Issue 1 of Teach Starter's Year 1 magazine.
Take the stress out of your literacy planning with these comprehensive task cards!
What are these task cards for?
These task cards have been designed specifically for use with Issue 1 of Teach Starter’s Year 1 magazine, What’s Buzzing?
How do I use the magazine and task cards for literacy groups?
In countless ways! You could assign each literary group an article for the week, then allow the students to work through the five sets of task cards.
Teachers, please read over the articles before you plan your activities. Some content may need teacher guidance depending on students’ abilities.
What types of task cards are included?
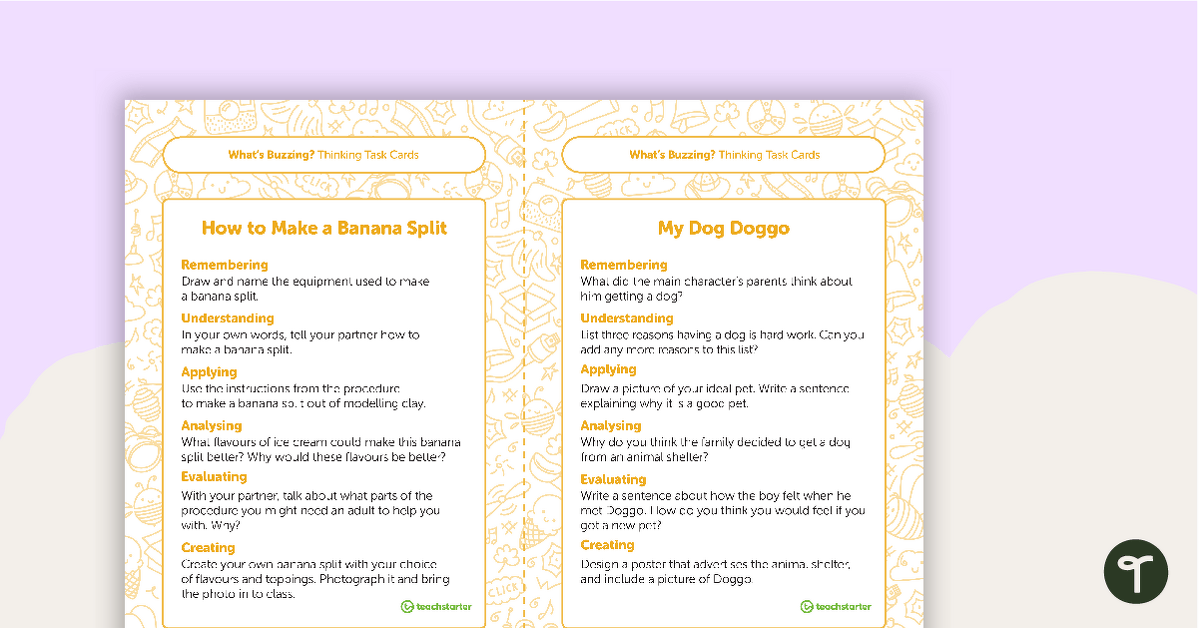
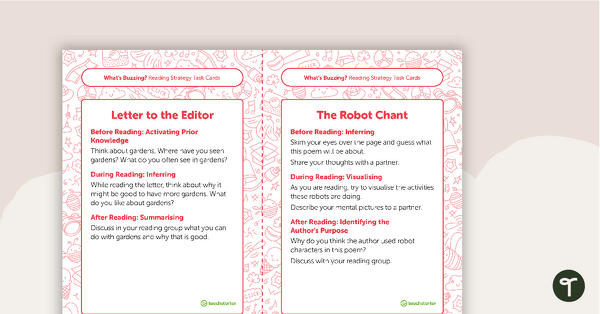
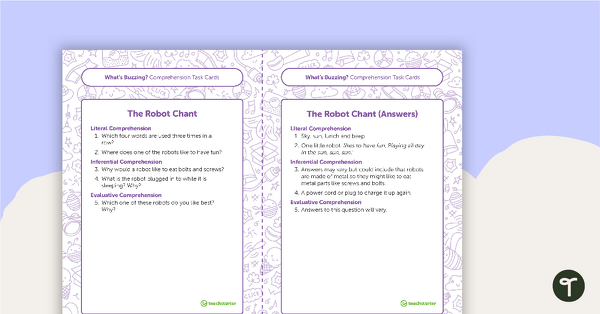
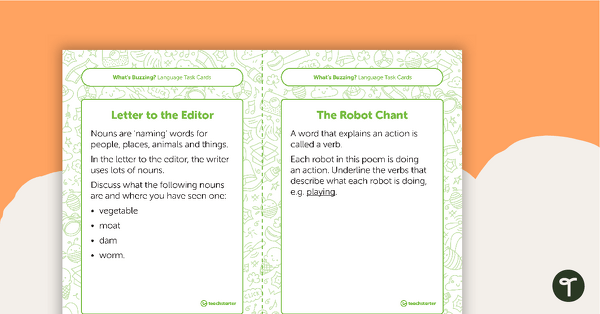
Five sets of task cards have been included. These address the areas of writing, language, comprehension, reading strategies and higher-order thinking skills.
Year 1 Magazine – What’s Buzzing (Issue 1)
You can access the magazine by clicking the thumbnail below.
[resource:3702602]












These are great resources! Any plans for making a foundation/kindergarten one?
Hey Emma, that sounds like a fantastic idea. We are currently observing the feedback for the current magazine issues to see where we go next with them. In the meantime, feel free to make a resource request. A high volume of votes helps the request gain traction and allows us to put into progress quicker.