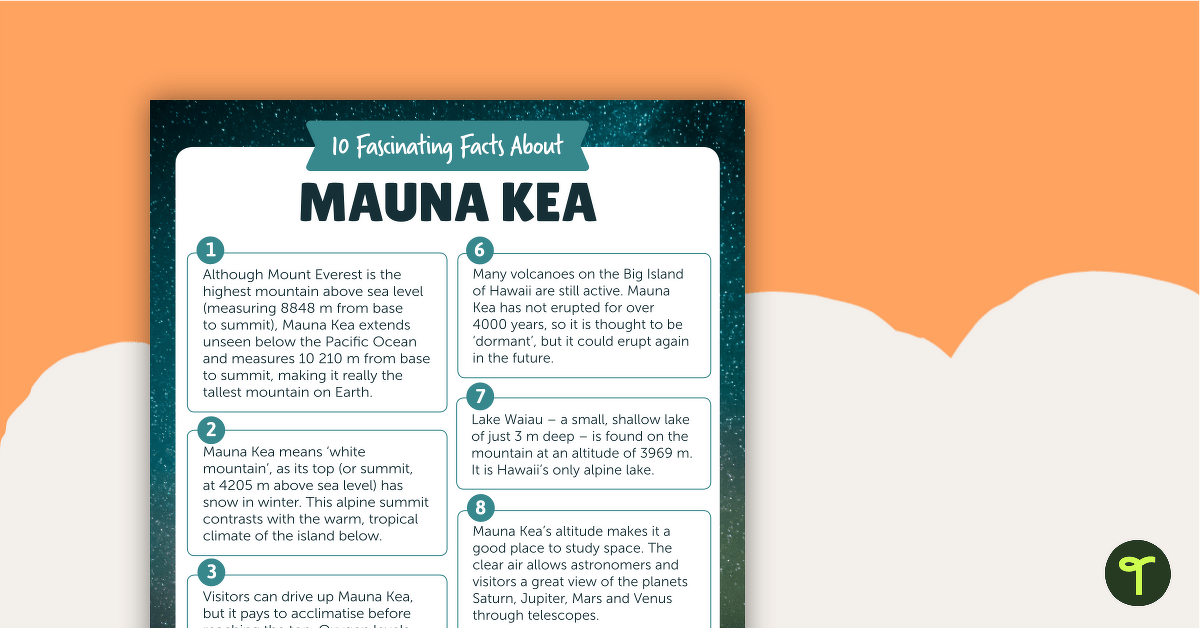
A comprehension worksheet for an article about ten facts about Mauna Kea in Hawaii.
This teaching resource is a comprehension worksheet asking questions about the magazine article, ’10 Fascinating Facts About Mauna Kea’.
In the text, students will learn about the amazing volcanic Big Island of Hawaii which includes the infamous mountain Mauna Kea.










Hi, is there an answer sheet to accompany this resource?
Hey Premila, thank you for taking the time to reach out to us. As this worksheet asks questions that require various responses, there is no answer sheet. However, if you would like to see one, may I ask that you make a change request on this resources webpage.