Math 6.8
Expressions, equations, and relationships. The student applies mathematical process standards to use geometry to represent relationships and solve problems. The student is expected to:
(A) extend previous knowledge of triangles and their properties to include the sum of angles of a triangle, the relationship between the lengths of sides and measures of angles in a triangle, and determining when three lengths form a triangle;
(B) model area formulas for parallelograms, trapezoids, and triangles by decomposing and rearranging parts of these shapes;
(C) write equations that represent problems related to the area of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and triangles and volume of right rectangular prisms where dimensions are positive rational numbers; and
(D) determine solutions for problems involving the area of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and triangles and volume of right rectangular prisms where dimensions are positive rational numbers.
- Free Plan
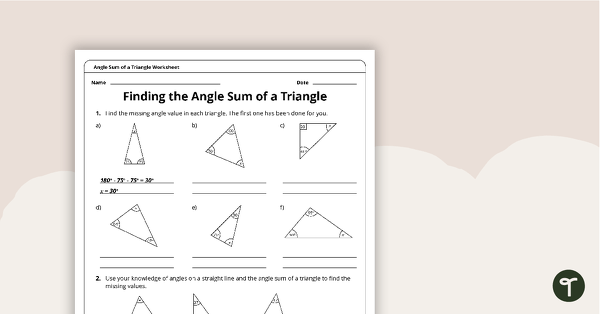
Angle Sum of a Triangle – 6th Grade Math Worksheet
Calculate the missing angle in a variety of triangles with this one-page worksheet.
- Plus Plan
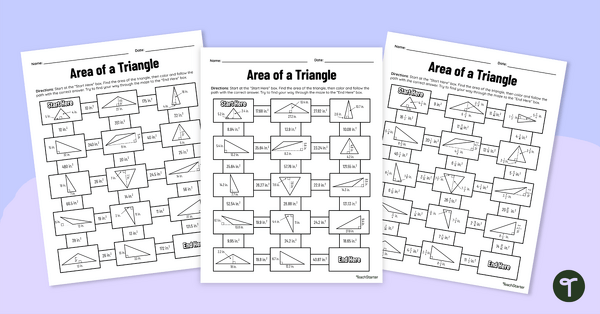
Area of a Triangle – Differentiated Math Mazes
Use the area of a triangle formula as you work your way through this set of differentiated math mazes.
- Plus Plan
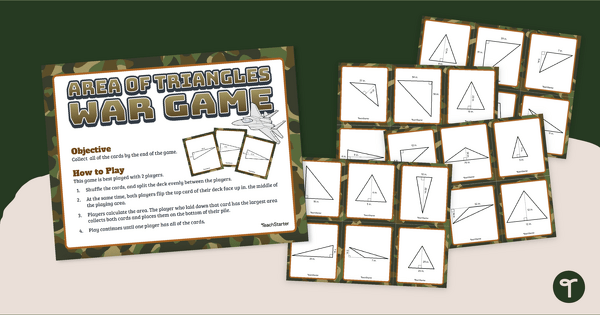
Triangle War - Area of a Triangle Math Game
Practice finding and comparing the area of a triangle with a game of WAR!
- Plus Plan
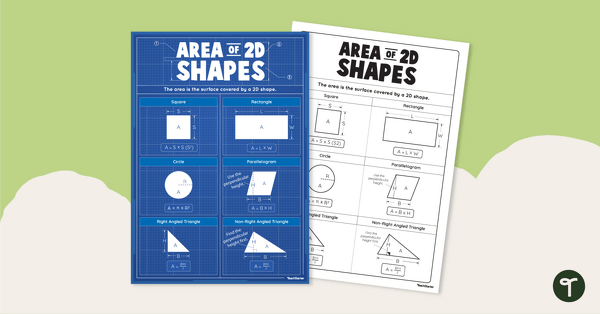
Area Formula for 2D Shapes Anchor Chart
Display this math poster showing the area formula for different 2D shapes during your geometry lessons.
- Plus Plan
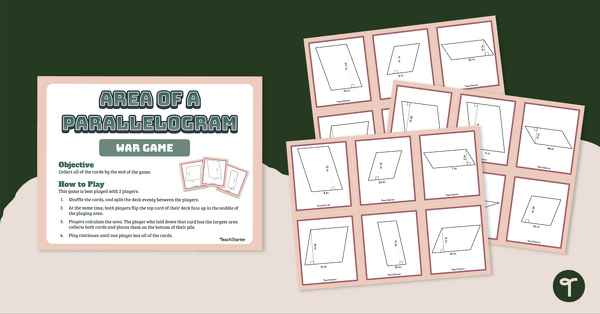
Area of a Parallelogram – War Game
Practice finding and comparing the area of a parallelogram with a game of WAR!
- Plus Plan
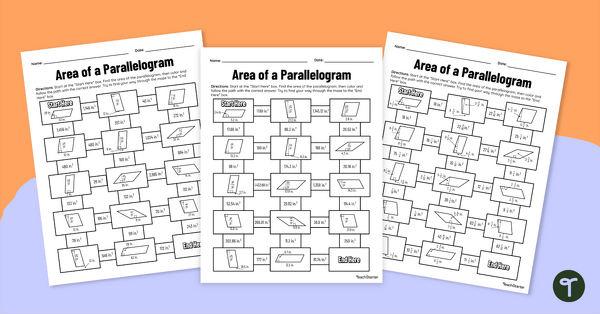
Area of a Parallelogram – Differentiated Math Mazes
Determine the area of different parallelograms with a set of differentiated math mazes.
- Plus Plan
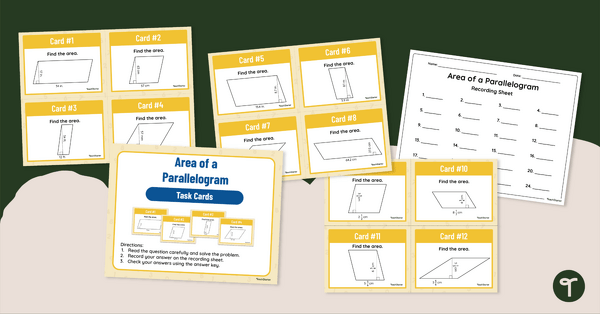
Area of a Parallelogram – Task Cards
Practice calculating the area of a parallelogram with this set of 24 task cards designed for 6th-grade students.
- Plus Plan
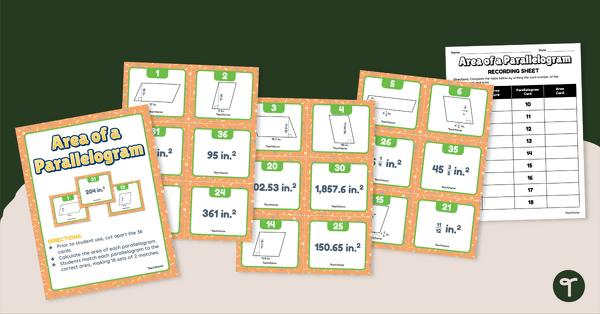
Area of a Parallelogram – Match-Up Activity
Calculate the area of parallelograms and match them with their corresponding areas with this match-up activity.
- Plus Plan
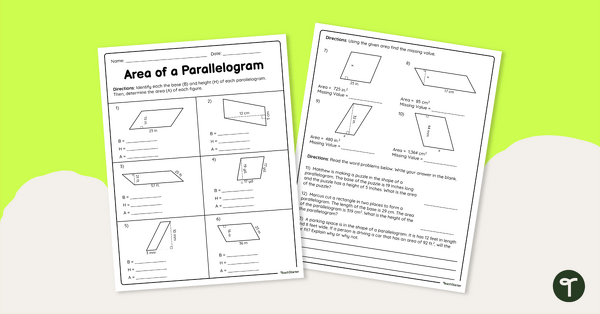
Area of a Parallelogram – Worksheet
Practice finding the area of a paralellogram with this math worksheet designed for 6th-grade students.
- Plus Plan

Area of a Triangle Matching Activity for 6th Grade
Calculate the area of triangle figures and match them with their corresponding areas with this match-up activity.
- Plus Plan
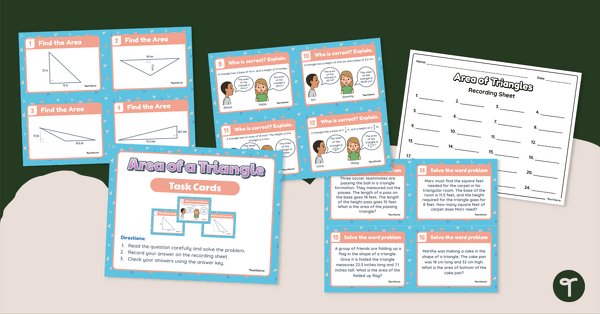
Area of a Triangle – Task Cards for 6th Grade
Sixth graders use multiplication and division skills to determine the area of a triangle with this set of 24 task cards.
- Plus Plan
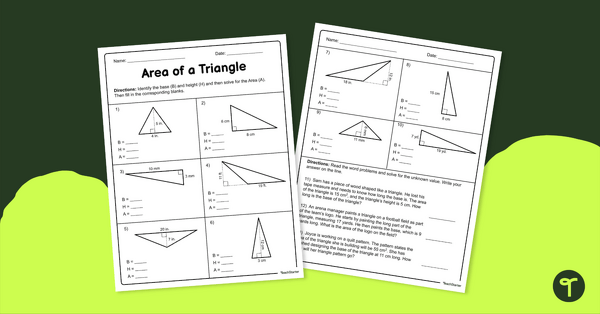
Area of a Triangle – Worksheet
Practice applying math formulas with this area of a triangle worksheet.
- Plus Plan
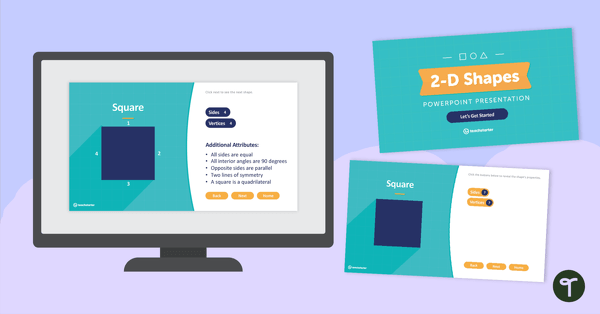
2-D Shapes and Their Attributes - Interactive PowerPoint
Practice identifying the attributes of different 2D shapes with this 90-slide interactive PowerPoint.
- Plus Plan

Up, Up, & Away! Volume of Rectangular Prisms – Google Slides Interactive Activity
Practice calculating the volume of rectangular prisms with this Google Slides interactive activity.
- Plus Plan
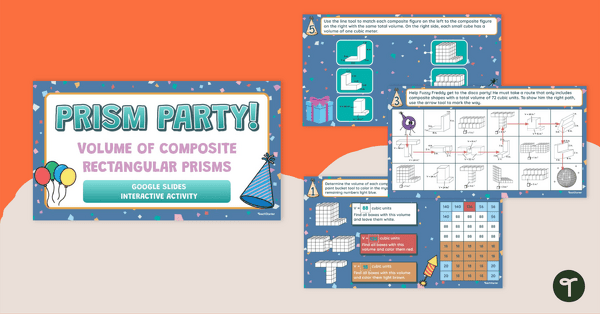
Prism Party! –Volume of Composite Rectangular Prisms – Google Slides Interactive Activity
Practice how to find the volume of composite figures with this interactive activity.
- Plus Plan
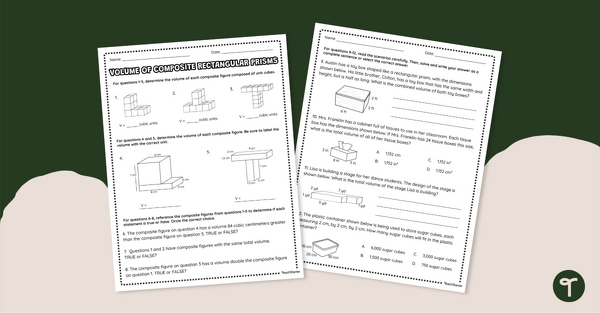
Volume of Composite Rectangular Prisms – Worksheet
Calculate the volume of composite figures and solve real-world problems with this worksheet.
- Plus Plan
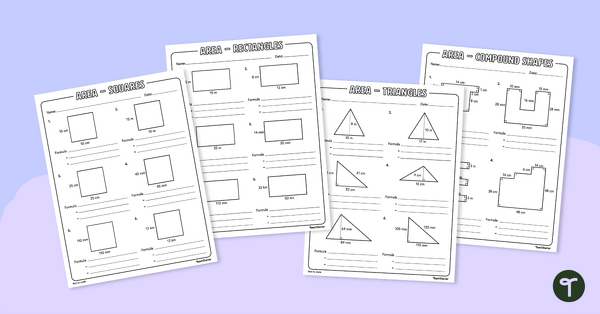
Area Worksheets
Practice finding the area of different shapes with this set of 4 worksheets.
- Plus Plan

Volume of Rectangular Prisms – Digital and Printable Worksheet
Practice finding the volume of rectangular prisms with a “This or That” worksheet.
- Plus Plan

Finding Volume (Differentiated Worksheets)
Teach finding the volume of rectangular prisms and cubes with this set of differentiated worksheets.
- Plus Plan

Interactive Area Puzzle (Triangles)
Set this task for students to find the area of 16 triangles on the board and match the corresponding pieces to reveal a mystery picture.
- Plus Plan

Grade 6 Daily Warm-Up – PowerPoint 3
A 70-slide PowerPoint presentation containing a variety of quick warm-up activities.
- Plus Plan
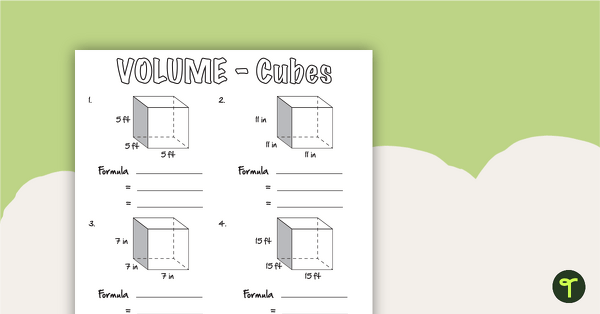
Volume of Three-Dimensional Objects Worksheets
Use this set of 3 volume worksheets when students need to practice solving using the volume formula.
- Plus Plan
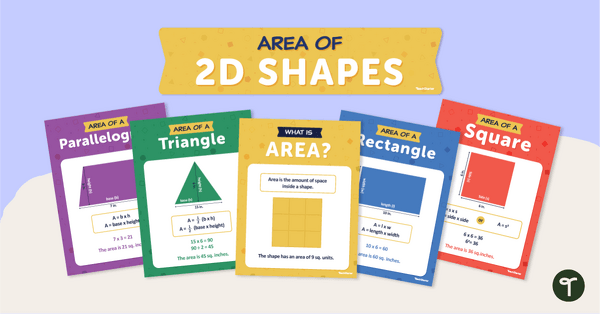
Area of 2D Shapes — Poster Set
Use this set of posters to teach how to find the area of 2D shapes.
- Plus Plan
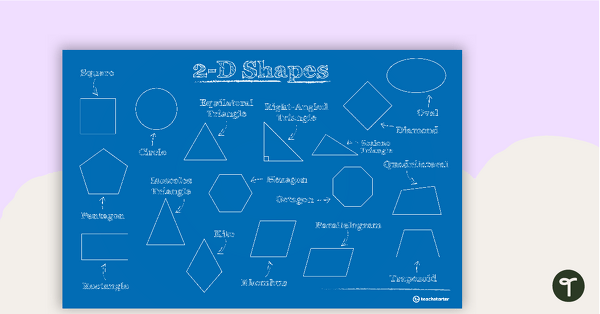
2-D Shapes – Poster
2-D shapes and their names on one poster.
- Plus Plan
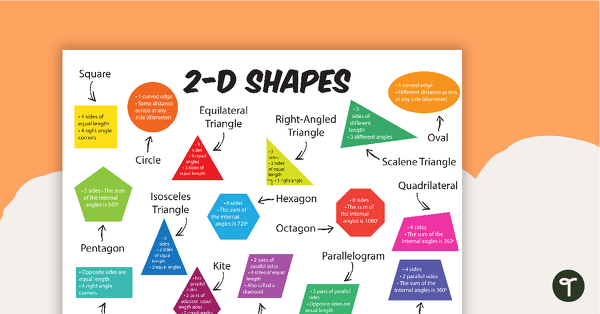
2-D Shapes with Information - Poster
A 2-D shapes poster with 16 common shapes, as well as information characterizing each shape.
- Plus Plan
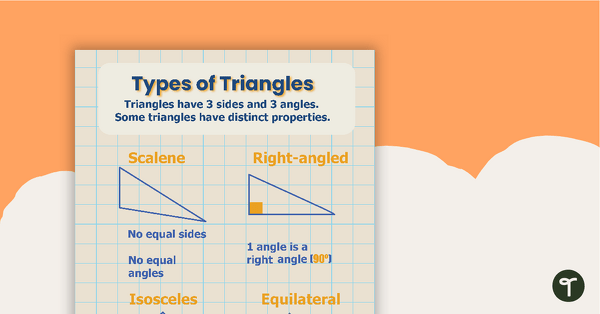
Types of Triangles Poster
A poster depicting and explaining the four types of triangles.