Number word problem worksheet with answers.
A mixed operations word problem worksheet with questions relating to number.
Answers with suggested working are also provided.
Updated: 16 Feb 2023
Number word problem worksheet with answers.
Non-Editable: PDF
Pages: 2 Pages
Years: 5 - 6
Tag #TeachStarter on Instagram for a chance to be featured!
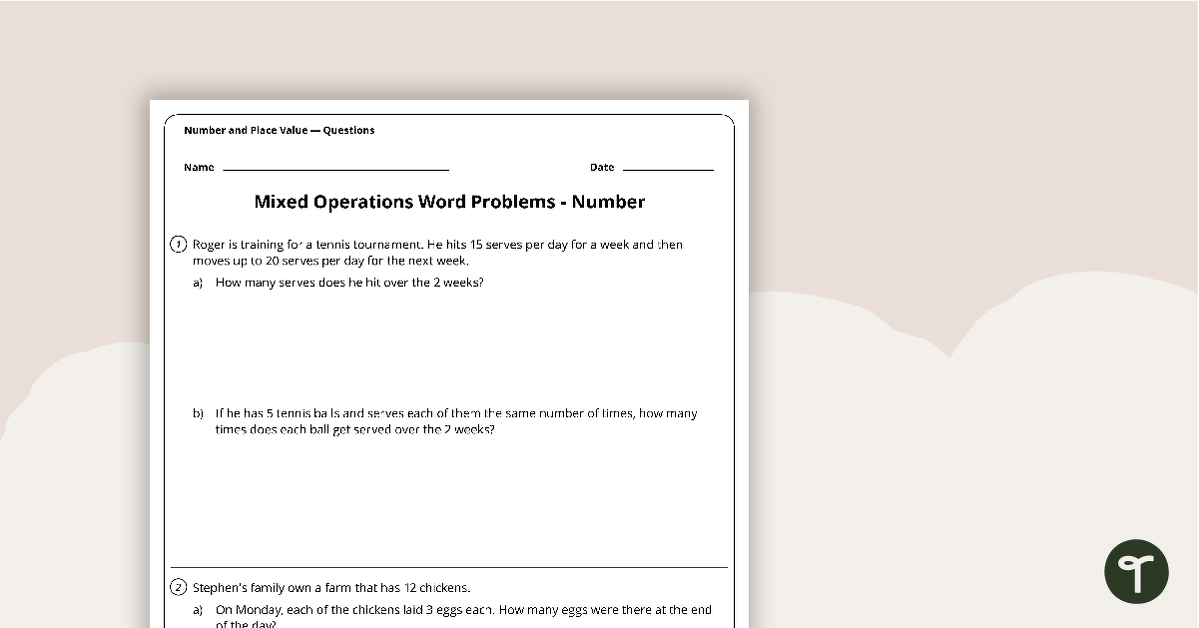
Number word problem worksheet with answers.
A mixed operations word problem worksheet with questions relating to number.
Answers with suggested working are also provided.

We create premium quality, downloadable teaching resources for primary/elementary school teachers that make classrooms buzz!
Fixed some incorrect answers and questions.
Would you like something changed or customised on this resource? While our team makes every effort to complete change suggestions, we can't guarantee that every change will be completed.
Did you spot an error on this resource? Please let us know and we will fix it shortly.
Are you having trouble downloading or viewing this resource? Please try the following steps:
If you are still having difficulty, please visit the Teach Starter Help Desk or contact us .
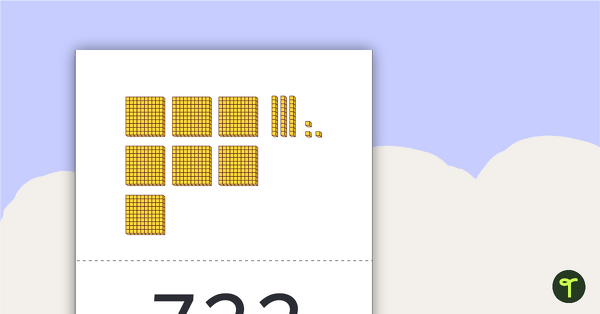
A set of 40 MAB flashcards of random numbers between 100 and 10000.

A set of place value cards to help students explore and expand larger numbers.
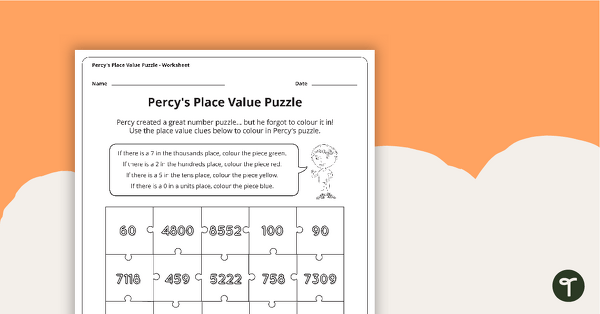
A worksheet to use to consolidate student understanding of place value to the thousands.
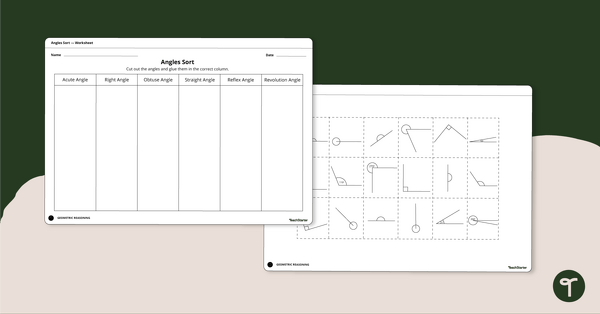
Identify acute, right, obtuse, straight, reflex and revolution angles with this cut-and-paste sorting worksheet.

Piggy Bank Pigs are a fun, hands on way for students to learn each of the coins and how their values add up to a certain amount.

Lower Grade Desk Plates with the alphabet, number line and student's name on them.

Area of 2D Shapes - so many rules and formulas to remember!
A mathematics investigation about location, embedded in a real-world context.
Use these area and perimeter task cards in your maths lessons to give your students practice solving real-world word problems.

A 14 page editable PowerPoint presentation to use when teaching number recognition to younger students.
0 Comments
Write a review to help other teachers and parents like yourself. If you'd like to request a change to this resource, or report an error, select the corresponding tab above.