Year 3
The science inquiry skills and science as a human endeavour strands are described across a two-year band. In their planning, schools and teachers refer to the expectations outlined in the achievement standard and also to the content of the science understanding strand for the relevant year level to ensure that these two strands are addressed over the two-year period. The three strands of the curriculum are interrelated and their content is taught in an integrated way. The order and detail in which the content descriptions are organised into teaching and learning programs are decisions to be made by the teacher.
Incorporating the key ideas of science
Over Years 3 to 6, students develop their understanding of a range of systems operating at different time and geographic scales.
In Year 3, students observe heat and its effects on solids and liquids and begin to develop an understanding of energy flows through simple systems. In observing day and night, they develop an appreciation of regular and predictable cycles. Students order their observations by grouping and classifying; in classifying things as living or non-living they begin to recognise that classifications are not always easy to define or apply. They begin to quantify their observations to enable comparison, and learn more sophisticated ways of identifying and representing relationships, including the use of tables and graphs to identify trends. They use their understanding of relationships between components of simple systems to make predictions.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
Achievement Standard
By the end of Year 3, students use their understanding of the movement of Earth, materials and the behaviour of heat to suggest explanations for everyday observations. They group living things based on observable features and distinguish them from non-living things. They describe how they can use science investigations to respond to questions.
Students use their experiences to identify questions and make predictions about scientific investigations. They follow procedures to collect and record observations and suggest possible reasons for their findings, based on patterns in their data. They describe how safety and fairness were considered and they use diagrams and other representations to communicate their ideas.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
- Plus Plan

Solids, Liquids and Gases PowerPoint
A 31 slide editable PowerPoint template to use when teaching your students about solids, liquids and gases.
- Plus Plan

Living and Non-Living Things Teaching Slides
Discover living and nonliving things with an engaging Living vs. Nonliving things teaching slide deck.
- Plus Plan

Living & Non-Living Things - Picture Sort
Sort biotic vs. abiotic things and discuss their characteristics with a hands-on living vs. nonliving picture sort.
- Plus Plan
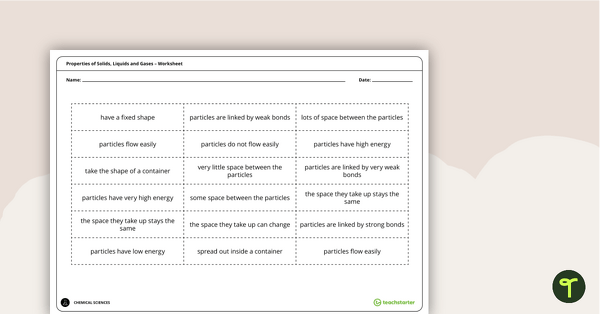
Properties of Solids, Liquids and Gases – Worksheet
A cut and paste activity that explores the properties of solids, liquids and gases.
- Free Plan

If I Could Create My Own Planet Craft Template
Explore planets and let your students get creative by developing their own planet.
- Plus Plan

Classification of Animals - PowerPoint
Teach your students about the different classes of animals and their characteristics with an Animal Classification teaching presentation.
- Plus Plan

Heat Sources Poster Set
Display these heat sources posters during your heat energy science unit.
- Plus Plan

Naked Mole Rat - Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Read and learn facts about the naked mole rat with a printable reading comprehension worksheet pack for year 4 and 5.
- Plus Plan
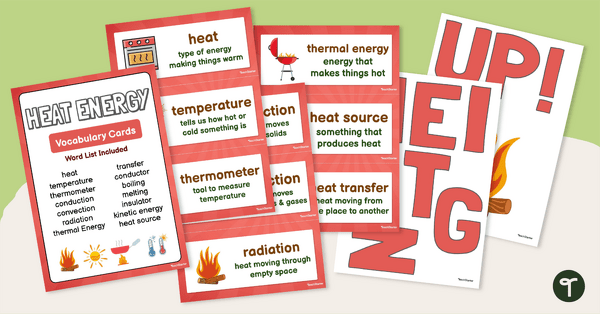
Year 3 Heat Energy Vocabulary Cards
Explore heat energy vocabulary with this set of thermal energy vocabulary cards.
- Plus Plan

Animal Classes Word Search Pack - Upper Years
Review vocabulary related to animal classes and characteristics of animals with a pack of printable animal classification word searches.
- Plus Plan
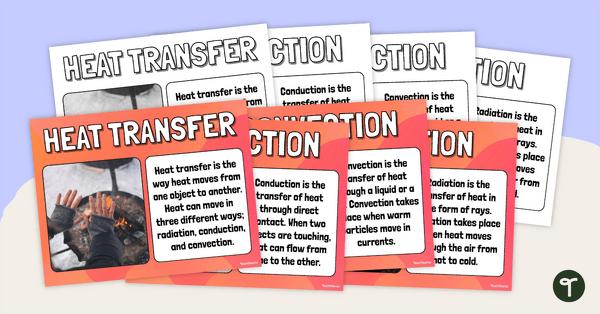
Heat Transfer Posters
Display these posters to check understanding or reinforce the teaching and learning of how heat energy transfers.
- Plus Plan

Earth's Rotation and Revolution – Teaching Presentation
Explore the difference between rotation and revolution while learning about the day and night cycle, what causes the seasons to change and more with this teaching presentation.
- Plus Plan
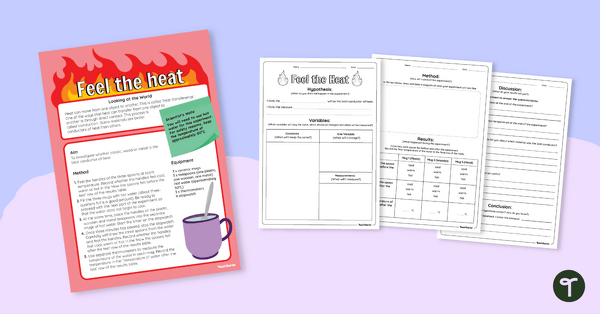
Heat Conductors Science Experiment (Feel the Heat)
Investigate heat conductors with your students using this engaging science experiment.
- Plus Plan
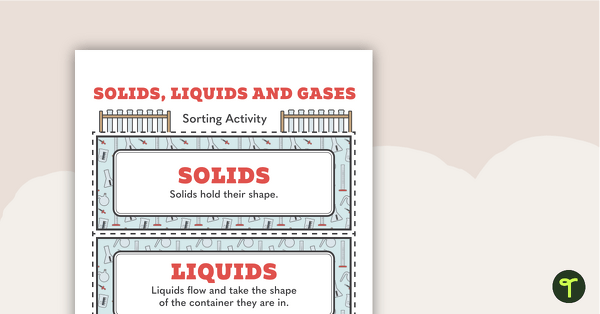
Solids, Liquids and Gases – Sorting Activity
A sorting activity to help students identify solids, liquids and gases.
- Plus Plan

Animal Adaptations - Informative Writing Prompt Worksheets
Write to describe animals and their adaptations with a printable pack of informative writing worksheets.
- Free Plan
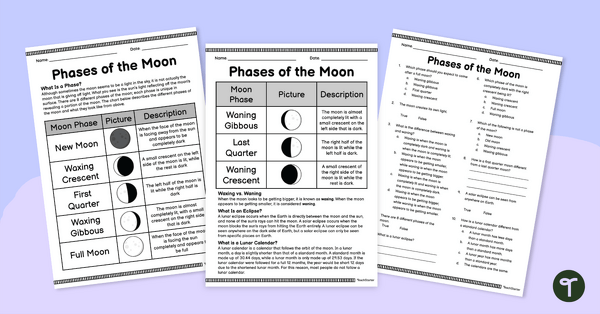
Phases of the Moon – Comprehension Worksheet
Analyse different moon phases and how their visual appearances change over time with this reading comprehension worksheet.
- Plus Plan
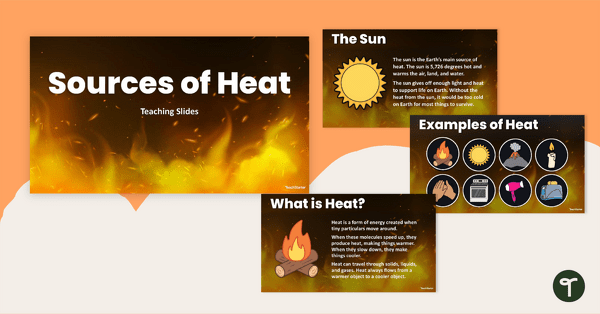
Sources of Heat Teaching Slides
Learn about the different sources of heat with this set of engaging teaching slides.
- Free Plan
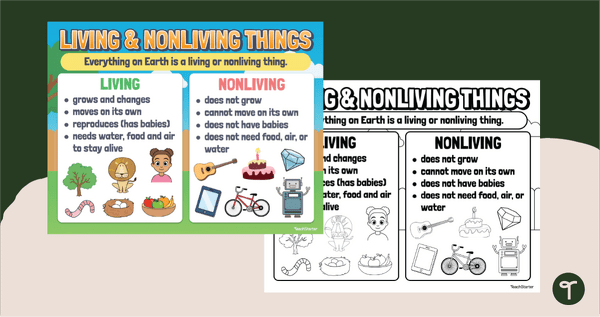
Living and Non-Living Things Poster
Highlight the differences between living and non-living things with an illustrative Living vs. Nonliving Things Anchor Chart
- Plus Plan

Planets Fact Sheets and Comprehension Worksheets
Learn the facts of each of the planets in our solar system with these fact files and matching comprehension worksheets.
- Plus Plan

Heat Sources Cut-and-Paste Worksheet
Explore different types of heat sources with your students using this cut-and-paste worksheet.
- Plus Plan
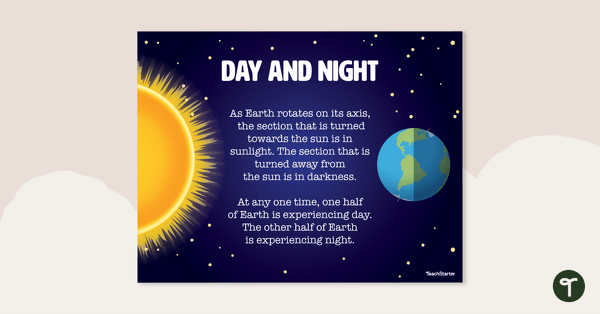
Day and Night Cycle Poster
Display information about Earth’s day and night cycle with this colourful science poster.
- Plus Plan

Earth, Sun and Moon – Poster Pack
Display these posters with information about the Earth, Sun and moon in your science classroom.
- Plus Plan

What Do Living Things Need to Survive? PowerPoint
Teach your students what living things need to survive with an engaging, interactive teaching slide deck.
- Free Plan

Changing States – Worksheet
A worksheet to consolidate your students' understanding of state changes from solid to liquid and liquid to solid.
- Plus Plan
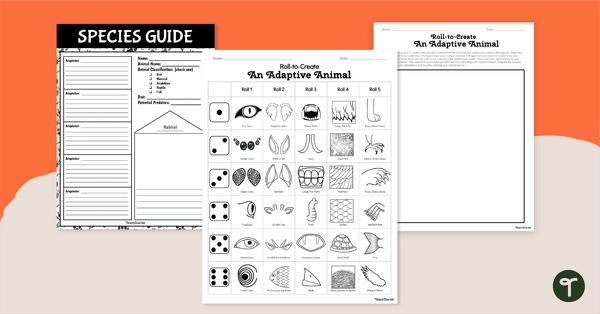
Roll to Create an Animal - Adaptations Game
Roll to create an animal with cool adaptations using a fun dice game and report template.
- Plus Plan
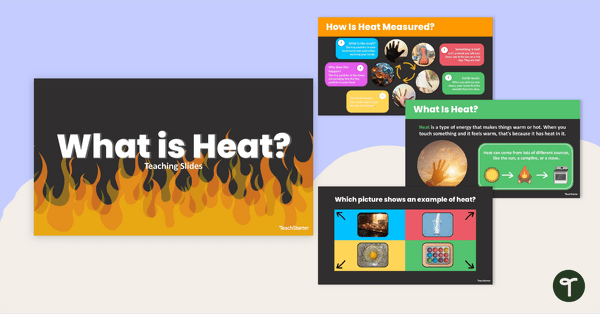
What is Heat? Thermal Energy Teaching Slides
Guide students through learning about thermal energy with this set of ‘What is Heat?’ teaching slides.
- Plus Plan
What is Heat? Worksheet
A worksheet to help students understand heat energy.
- Free Plan

Free Planet Colouring Pages
Use these black and white planet templates as colouring in pages for your students.
- Plus Plan

Earth and Space Vocabulary Posters
Display this set of 18 mini-posters in your classroom when learning about Earth and space vocabulary.
- Plus Plan

Living or Non-living Things – Interactive Activity
Identify living and non-living things with this self-checking interactive activity.
- Plus Plan
Heat Transference Worksheet
A worksheet to help students identify examples of heat transference.
- Plus Plan

Heat Insulators Science Experiment (Keeping Out the Heat)
Investigate heat insulators with your students using this engaging science experiment.