A project where students use their mathematic skills to plan a fundraiser for a charity of choice.
This open-ended mathematics investigation has been designed to deepen students’ understanding of financial mathematics.
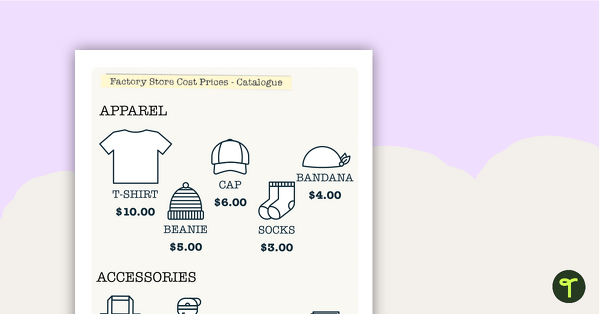
The scenario involves selling uniquely designed merchandise to fundraise for a charity of choice.
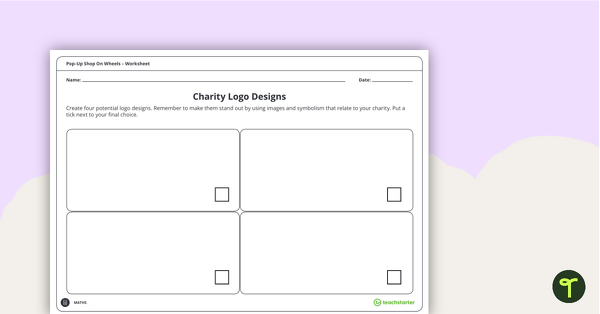
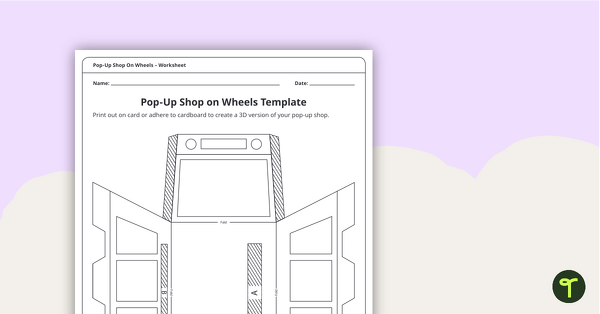
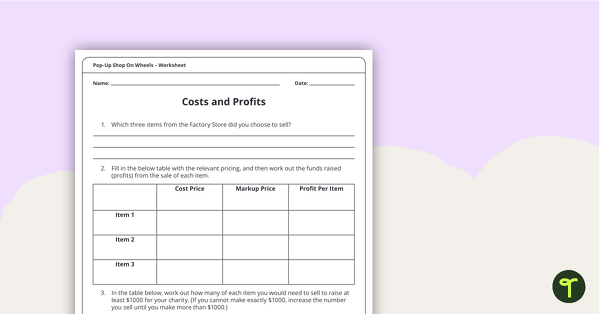
Students design a logo to represent ideas related to their chosen charity. Once they have chosen a design, they will need to apply it to three types of merchandise, plus a pop-up shop in the form of a truck. Students will then need to use their money and finances skills to calculate how many items they need to sell in order to make a profit.




0 Comments
Write a review to help other teachers and parents like yourself. If you'd like to request a change to this resource, or report an error, select the corresponding tab above.