Years 5 and 6
Learning in Digital Technologies focuses on further developing understanding and skills in computational thinking such as identifying similarities in different problems and describing smaller components of complex systems. It also focuses on the sustainability of information systems for current and future uses.
By the end of Year 6, students will have had opportunities to create a range of digital solutions, such as games or quizzes and interactive stories and animations.
In Year 5 and 6, students develop an understanding of the role individual components of digital systems play in the processing and representation of data. They acquire, validate, interpret, track and manage various types of data and are introduced to the concept of data states in digital systems and how data are transferred between systems.
They learn to further develop abstractions by identifying common elements across similar problems and systems and develop an understanding of the relationship between models and the real-world systems they represent.
When creating solutions, students define problems clearly by identifying appropriate data and requirements. When designing, they consider how users will interact with the solutions, and check and validate their designs to increase the likelihood of creating working solutions. Students increase the sophistication of their algorithms by identifying repetition and incorporate repeat instructions or structures when implementing their solutions through visual programming, such as reading user input until an answer is guessed correctly in a quiz. They evaluate their solutions and examine the sustainability of their own and existing information systems.
Students progress from managing the creation of their own ideas and information for sharing to working collaboratively. In doing so, they learn to negotiate and develop plans to complete tasks. When engaging with others, they take personal and physical safety into account, applying social and ethical protocols that acknowledge factors such as social differences and privacy of personal information. They also develop their skills in applying technical protocols such as devising file naming conventions that are meaningful and determining safe storage locations to protect data and information.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
Achievement Standard
By the end of Year 6, students explain how social, ethical, technical and sustainability considerations influence the design of solutions to meet a range of present and future needs. They explain how the features of technologies influence design decisions and how digital systems are connected to form networks.
Students describe a range of needs, opportunities or problems and define them in terms of functional requirements. They collect and validate data from a range of sources to assist in making judgements. Students generate and record design ideas for specified audiences using appropriate technical terms, and graphical and non-graphical representation techniques including algorithms. They plan, design, test, modify and create digital solutions that meet intended purposes including user interfaces and a visual program. Students plan and document processes and resources and safely produce designed solutions for each of the prescribed technologies contexts. They negotiate criteria for success, including sustainability considerations, and use these to judge the suitability of their ideas, solutions and processes. Students use ethical, social and technical protocols when collaborating, and creating and communicating ideas, information and solutions face-to-face and online.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
Achievement Standard
By the end of Year 6, students explain the fundamentals of digital system components (hardware, software and networks) and how digital systems are connected to form networks. They explain how digital systems use whole numbers as a basis for representing a variety of data types.
Students define problems in terms of data and functional requirements and design solutions by developing algorithms to address the problems. They incorporate decision-making, repetition and user interface design into their designs and implement their digital solutions, including a visual program. They explain how information systems and their solutions meet needs and consider sustainability. Students manage the creation and communication of ideas and information in collaborative digital projects using validated data and agreed protocols.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
- Plus Plan
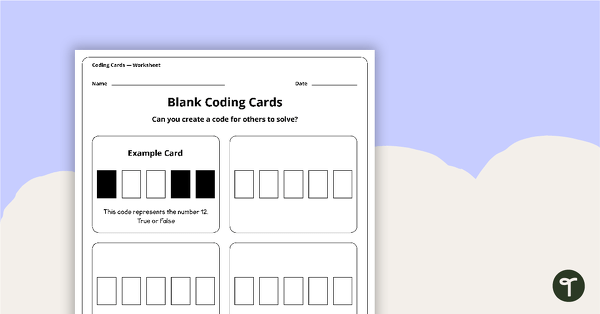
Blank Binary Coding Cards - Worksheet
A worksheet to assist students in creating their own binary codes.
- Free Plan
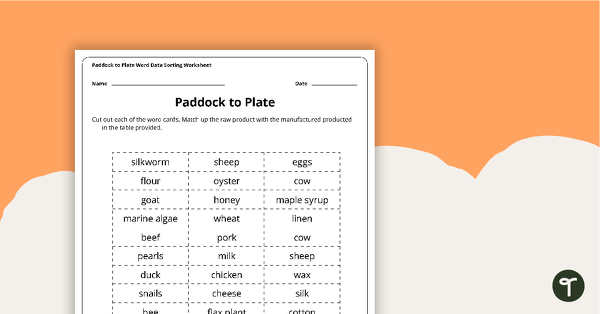
Paddock to Plate Data Sorting Worksheet
A cut and paste sorting worksheet for use when learning about raw and manufactured products.
- Plus Plan
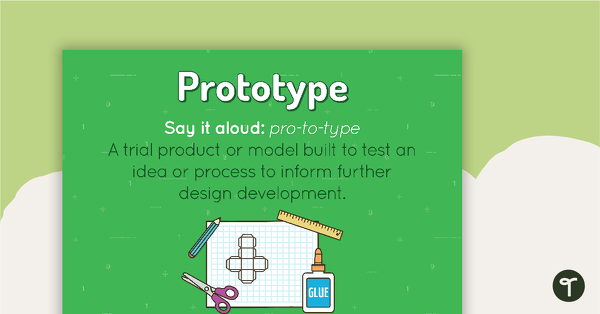
Prototype Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of a prototype.
- Free Plan

Code Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of code.
- Plus Plan

Coding Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of coding.
- Plus Plan
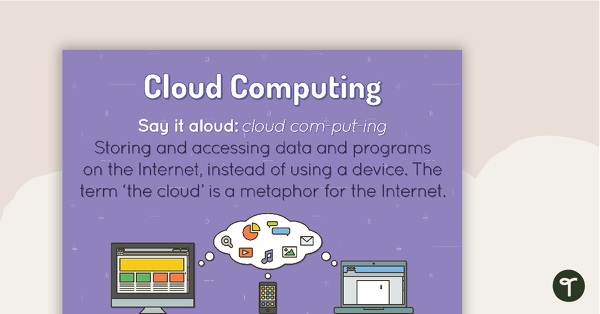
Cloud Computing Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of cloud computing.
- Free Plan

Binary Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of binary.
- Plus Plan

8-bit Coding Card Packs with Activities
A set of 8-bit coding cards with associated activities to assist students in understanding 8-bit coding.
- Plus Plan
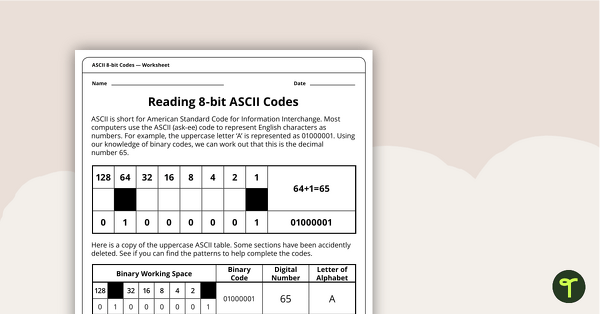
Reading 8-bit ASCII Codes - Worksheet
A worksheet to assist students in understanding what actual computer code (ASCII- current 8-bit version) looks like.
- Plus Plan

8-bit Decoding Puzzle
A puzzle for students to solve when consolidating their understanding of coding.
- Plus Plan

Binary Codes to 20 without Guide Dots - Worksheet
An activity for students to complete when learning how to read and write in code.
- Plus Plan
Binary Coding Cards
Use these binary coding cards to demonstrate how to ‘switch’ a ‘digit’ on or off.
- Plus Plan

Class 'We Can' Statements - Technology and Technologies (Upper Primary)
A set of 28 class 'We can' statement cards linked to the Australian Digital Technologies Curriculum.
- Plus Plan
'I Can' Statements - Technology and Technologies (Upper Elementary)
A set of 45 'I can' statement cards.
- Plus Plan

'I Can' Statements - Technology and Technologies (Upper Primary)
A set of 45 'I can' statement cards linked to the Australian Digital Technologies Curriculum.
- Plus Plan
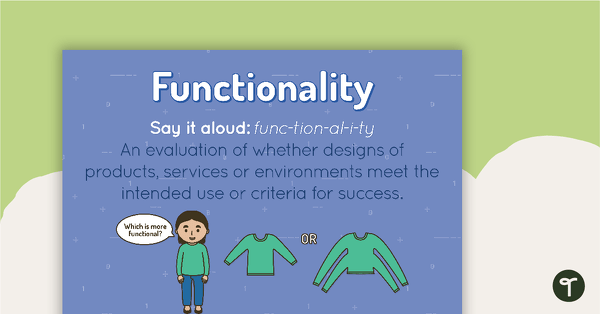
Functionality Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of Functionality.
- Plus Plan
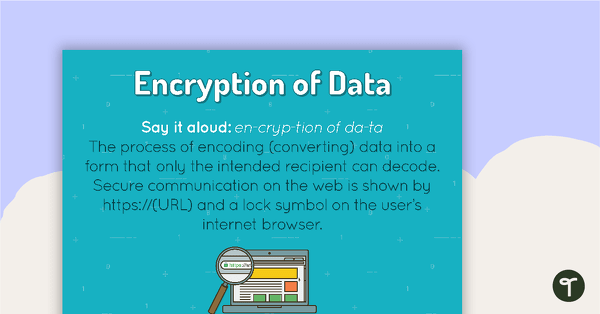
Encryption of Data Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of data encryption.
- Plus Plan

Social Sustainability Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of social sustainability.
- Plus Plan
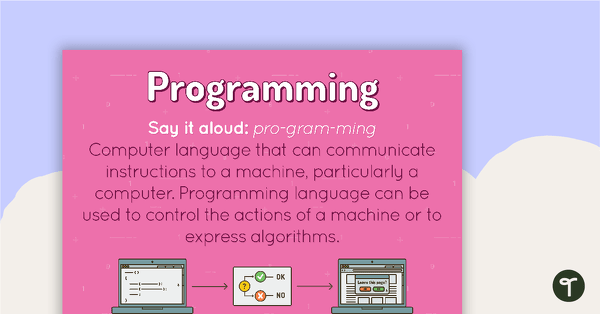
Programming Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of programming.
- Plus Plan

8Ws of Project Development (Technologies) - Individual Posters
A poster for teachers to display and discuss when helping students to develop a project.
- Plus Plan

8Ws of Project Development Poster (Technologies)
A poster for teachers to display and discuss when helping students to develop a project.
- Plus Plan
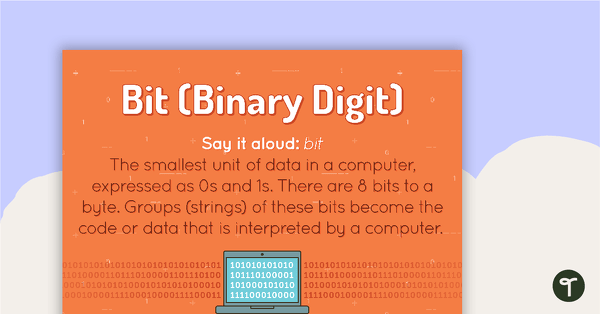
Bit Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of a bit.
- Free Plan
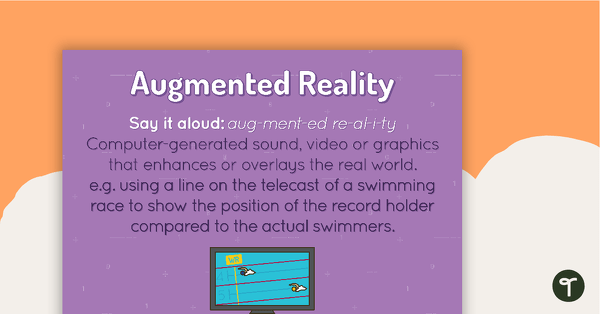
Augmented Reality Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of an augmented reality.
- Plus Plan
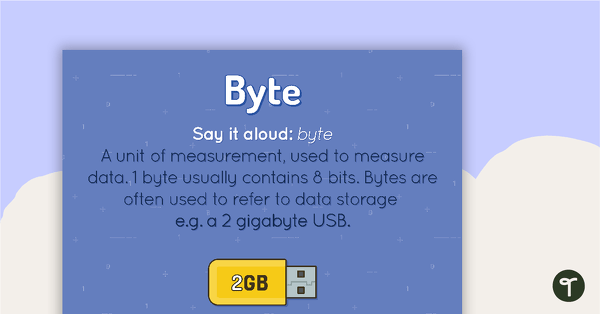
Byte Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of a byte.
- Plus Plan

ASCII Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of ASCII.
- Plus Plan
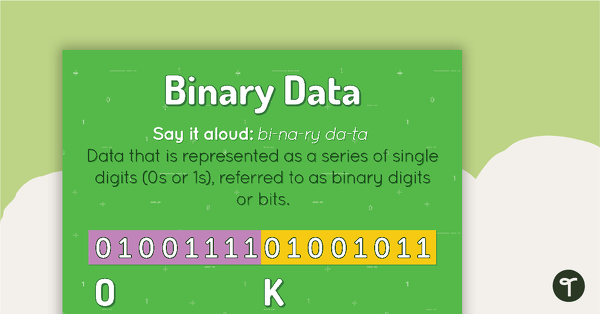
Binary Data Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of binary data.
- Plus Plan

Sustainability Criteria Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of sustainability criteria.
- Plus Plan
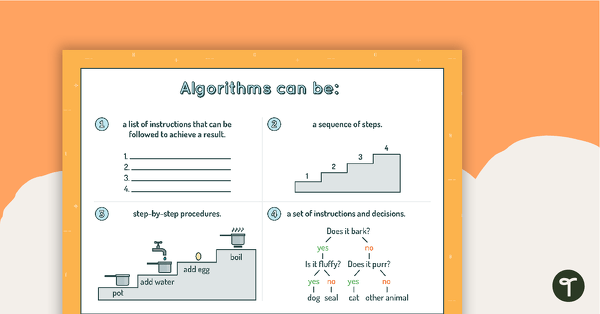
Algorithms Can Be... Poster
A poster showing the different forms algorithms can take.
- Plus Plan

Reinforcing 8-bit Coding
A 60 minute lesson in which students will develop confidence in identifying and exploring coding data.