Years 3 and 4
Learning in Digital Technologies focuses on further developing understanding and skills in computational thinking, such as categorising and outlining procedures; and developing an increasing awareness of how digital systems are used and could be used at home, in school and the local community.
By the end of Year 4, students will have had opportunities to create a range of digital solutions, such as interactive adventures that involve user choice, modelling simplified real world systems and simple guessing games.
In Year 3 and 4, students explore digital systems in terms of their components, and peripheral devices such as digital microscopes, cameras and interactive whiteboards. They collect, manipulate and interpret data, developing an understanding of the characteristics of data and their representation.
Using the concept of abstraction, students define simple problems using techniques such as summarising facts to deduce conclusions. They record simple solutions to problems through text and diagrams and develop their designing skills from initially following prepared algorithms to describing their own that support branching (choice of options) and user input. Their solutions are implemented using appropriate software including visual programming languages that use graphical elements rather than text instructions. They explain, in general terms, how their solutions meet specific needs and consider how society may use digital systems to meet needs in environmentally sustainable ways.
With teacher guidance, students identify and list the major steps needed to complete a task or project. When sharing ideas and communicating in online environments they develop an understanding of why it is important to consider the feelings of their audiences and apply safe practices and social protocols agreed by the class that demonstrate respectful behaviour.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
Achievement Standard
By the end of Year 4, students describe how social, technical and sustainability factors influence the design of solutions to meet present and future needs. They describe features of technologies that influence design decisions and how a range of digital systems can be used.
Students outline and define needs, opportunities or problems. They collect, manipulate and interpret data from a range of sources to support decisions. Students generate and record design ideas for an audience using technical terms and graphical and non-graphical representation techniques including algorithms. They plan a sequence of steps (algorithms) to create solutions, including visual programs. Students plan and safely produce designed solutions for each of the prescribed technologies contexts. They use identified criteria for success, including sustainability considerations, to judge the suitability of their ideas, solutions and processes. Students use agreed protocols when collaborating, and creating and communicating ideas, information and solutions face-to-face and online.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
Achievement Standard
By the end of Year 4, students describe how a range of digital systems (hardware and software) and their peripheral devices can be used for different purposes. They explain how the same data sets can be represented in different ways.
Students define simple problems, design and implement digital solutions using algorithms that involve decision-making and user input. They explain how the solutions meet their purposes. They collect and manipulate different data when creating information and digital solutions. They safely use and manage information systems for identified needs using agreed protocols and describe how information systems are used.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
- Free Plan
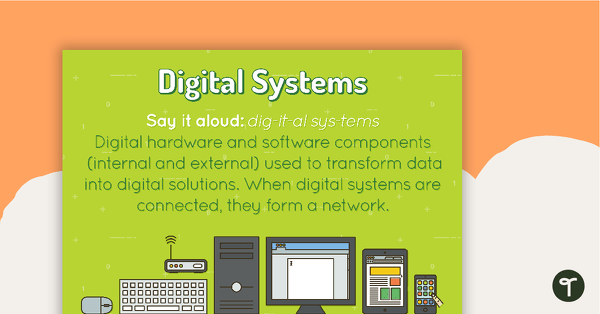
Digital Systems Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of a digital system.
- Free Plan
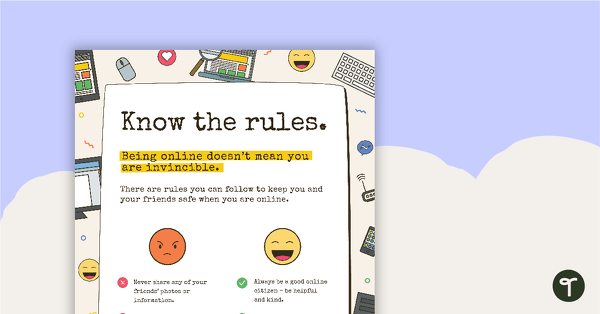
Cyber Safety Poster - Know the Rules
A cyber safety poster to help the students understand correct online behaviour.
- Free Plan

Occupations in Design and Technology Match-Up Activity
A match-up game linking occupations and the technologies required to successfully perform the job.
- Free Plan

Binary Codes to 20 with Guide Dots - Worksheet
An activity for students to complete when learning how to read and write in code.
- Plus Plan
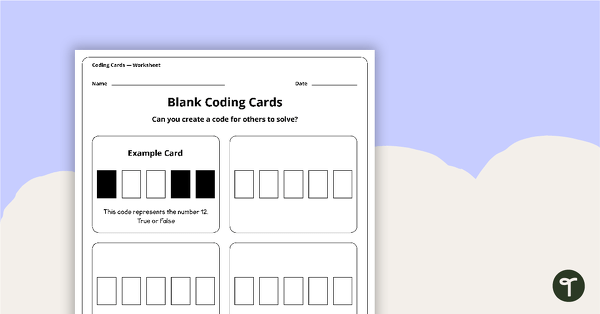
Blank Binary Coding Cards - Worksheet
A worksheet to assist students in creating their own binary codes.
- Plus Plan
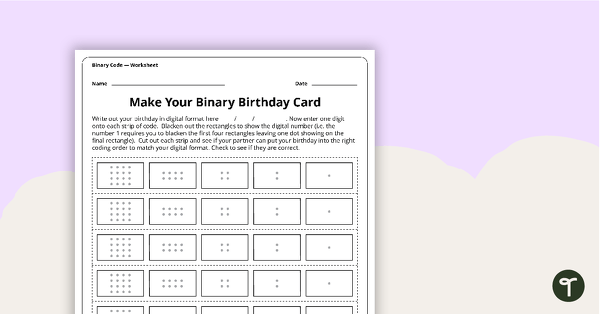
Make Your Binary Code Birthday Card Activity
A worksheet for students to use when learning about the total numeric value of a bit code.
- Plus Plan
Cyber Safety Poster – Keep Your Details Safe
A cyber safety poster to help the students understand correct online behaviour.
- Plus Plan

Materials Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of materials.
- Plus Plan
Data Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of data.
- Plus Plan
Algorithm Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of an algorithm.
- Plus Plan

Life Changing Technologies - Match-Up Activity
A match-up activity linking technologies and technological devices with the function they perform.
- Plus Plan

Binary Codes Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of binary codes.
- Free Plan

Binary Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of binary.
- Free Plan

Friend or Foe? Positive and Negative Effects of Technology Worksheet
Exploring the positive and negative effects of technology in the community with classroom discussion and worksheets.
- Plus Plan

8-bit Coding Card Packs with Activities
A set of 8-bit coding cards with associated activities to assist students in understanding 8-bit coding.
- Plus Plan
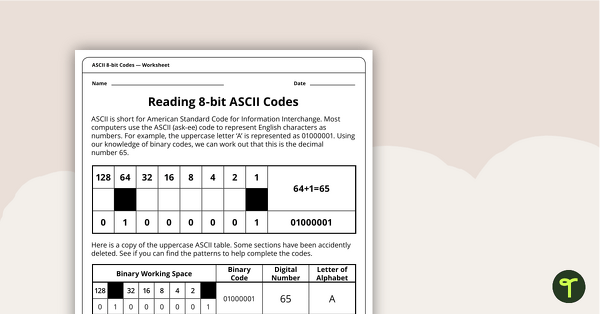
Reading 8-bit ASCII Codes - Worksheet
A worksheet to assist students in understanding what actual computer code (ASCII- current 8-bit version) looks like.
- Plus Plan

Binary Codes to 20 without Guide Dots - Worksheet
An activity for students to complete when learning how to read and write in code.
- Plus Plan

Cyber Safety Poster - Don't Be a Bystander
A cyber safety poster to help the students understand correct online behaviour.
- Plus Plan

Word Processing Activity Cards
16 activity cards for students to use to practise their word processing skills.
- Free Plan
Paddock to Plate Data Sorting Worksheet
A cut and paste sorting worksheet for use when learning about raw and manufactured products.
- Plus Plan
Input/Output Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of an input and an output.
- Free Plan
Technology Workstation Worksheet - Tablet
A worksheet for students to label the key components of a tablet workstation.
- Plus Plan
Data Match-Up Cards (Set 1)
A match-up activity for students to use when exploring data.
- Plus Plan
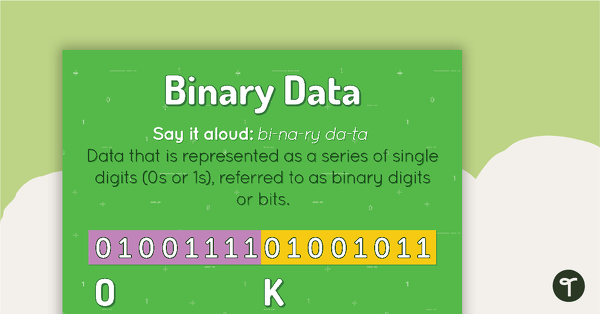
Binary Data Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of binary data.
- Plus Plan

Classmate Coding - Flashcards and Activities
Introduce your students to the concept of coding by having them "program" a classmate using coding cards.
- Plus Plan
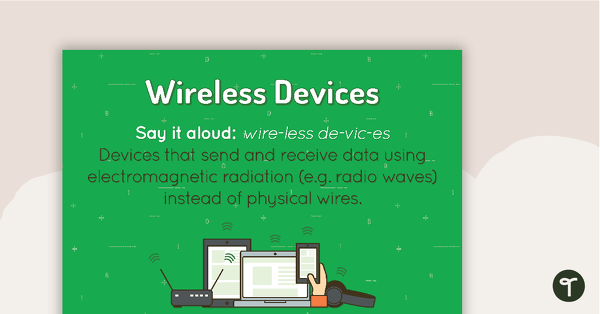
Wireless Devices Poster
A poster showing the definition and visual representations of wireless devices.
- Plus Plan
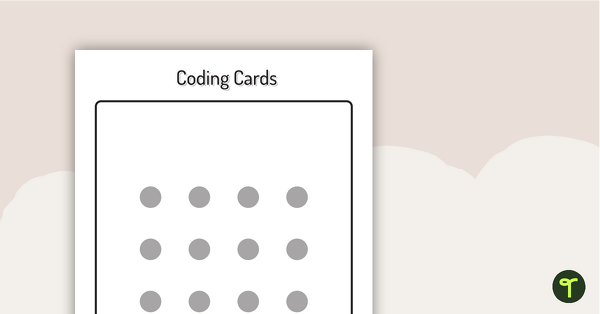
Binary Coding Cards
Use these binary coding cards to demonstrate how to ‘switch’ a ‘digit’ on or off.
- Plus Plan
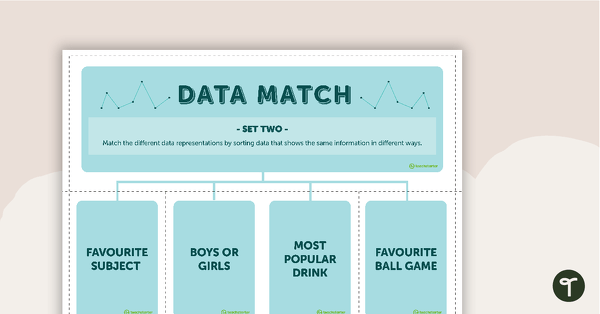
Data Match-Up Cards (Set 2)
A match-up activity for students to use when exploring data.
- Plus Plan
Data Match-Up Cards (Set 5)
A match-up activity for students to use when exploring data.
- Plus Plan
Positive Impacts of Technology Worksheet
Exploring the positive impacts of technology in the community with a pair of printable worksheets.
- Plus Plan

Word Processing Skills Task Cards
48 skills cards for students to use to enhance their word processing skills.
- Plus Plan

Occupations and Sustainability in Technology Assessment
A four-page assessment task covering occupations and sustainability in technology.