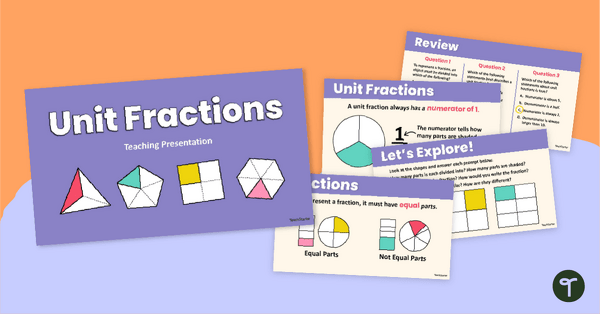
Use this teaching presentation to teach your students how to identify the parts of a fraction, determine equal and unequal parts and use numerators and denominators to write fractions.
Understanding Fractions
Did you know that students start to begin their understanding of fractions as early as year 2? You may be wondering, how is that possible? Students in this year level aren’t working with fractions in a traditional sense but are building the foundation of understanding how shapes can be divided into equal and unequal parts and that these parts can be identified with words (halves, fourths, eighths, etc.). As students move into year 3, they work on understanding how visual models and numerically written fractions work hand-in-hand before solely working with ‘just the numbers.’
If you are just starting out with your fractions unit (or perhaps your students are in need of a refresher), Teach Starter has you covered! With this 19-slide interactive teaching presentation, students will be introduced to basic fraction concepts. Students will explore concepts such as:
- What are fractions?
- equal and unequal parts
- parts of a fraction
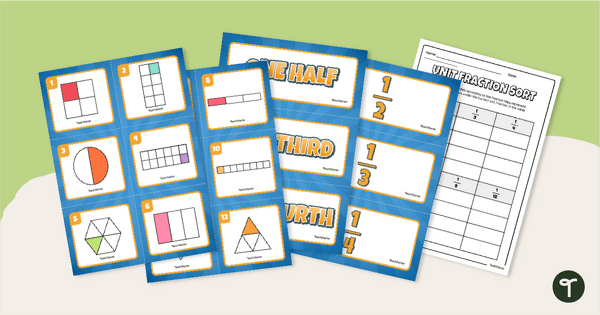
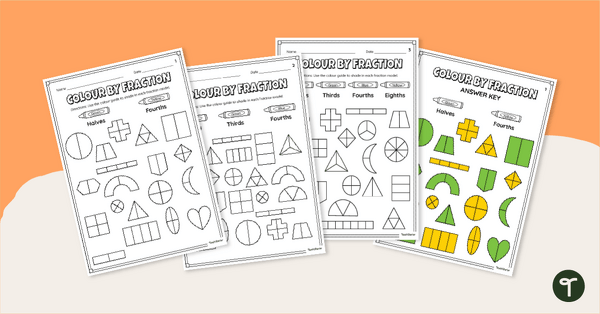
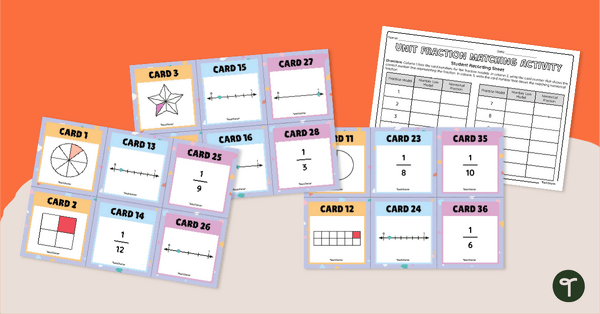
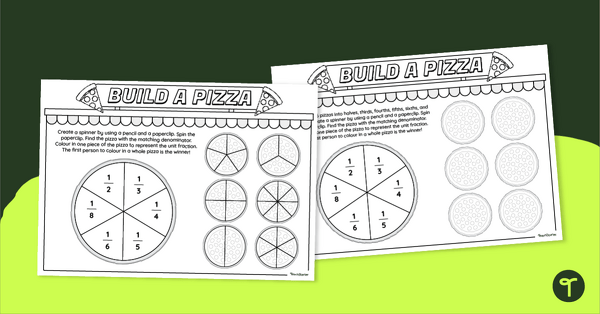
- understanding halves, thirds, fourths, fifths, sixths and eighths
- naming fractions
When working through this presentation with your students, please note that there are some interactive activities (typing in numbers, drag and drop, etc.). You can choose to complete these activities in edit mode or use a drawing tool on an interactive whiteboard to complete the activities by drawing circles, writing numbers, etc.
Tips for Differentiation + Scaffolding
A team of dedicated, experienced educators created this resource to support your maths lessons.
This teaching presentation can be used to support your whole class lessons or remote learning assignments.
If you have a mixture of above and below-level learners, check out these suggestions for keeping students on track with the concepts:
🆘 Support Struggling Students
For students who need extra support, allow them to reference the instructional slides as a resource when working with fractions. Additionally, consider giving students fraction circles or fraction bars to observe the size of the pieces, count the number of pieces to make a whole, etc.
➕ Challenge Fast Finishers
If there are students who need an additional challenge, encourage them to describe a real-life scenario involving fractions and ask students to draw a picture and write a fraction to illustrate the scenario.
Easily Prepare This Resource for Your Students
Use the dropdown icon on the Download button to choose between the Powerpoint or Google Slides version of this resource.
This resource was created by Lindsey Phillips, a Teach Starter Collaborator.




2 Comments
Write a review to help other teachers and parents like yourself. If you'd like to request a change to this resource, or report an error, select the corresponding tab above.
No comments yet.